invivoid® Technology
Methodology 1 :
CVA(Cell Viscous Assembly) Method
How it works
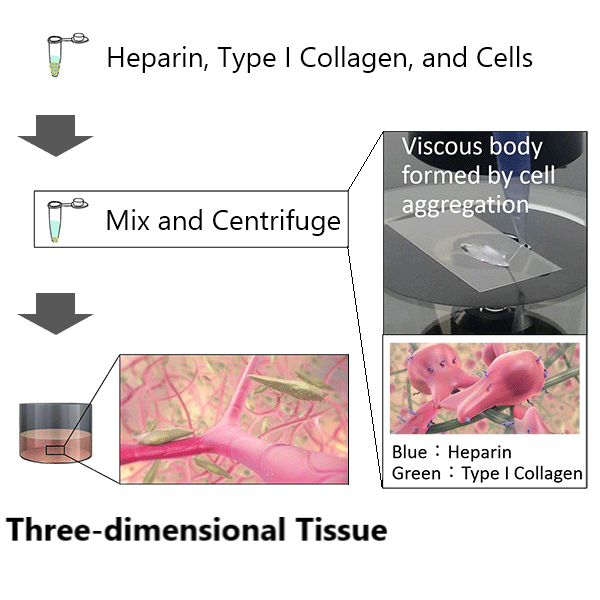
By adding heparin and type I collagen to cell suspension, a viscous body is formed by the strong aggregation of cells after centrifugation. Adhesion of cells is induced by the collagen, resulting in three-dimensional tissue. Various types of cells in the tissue mutually interact and align themselves, creating tissue with structures such as a network of capillary blood vessels.
A layer of cells up to 300 μm thickness can be fabricated in one step. Tissues with multi-layer structure can easily be constructed by repeating this step.
Key Advantages
Layered Co-Culture
Cell positions in layered tissue can be designed, constructed, and maintained during culture.
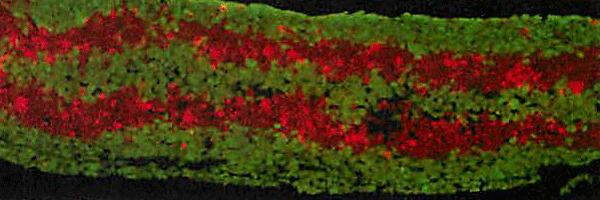
Example of tissue with five-layer structure
Self-Assembled Structures
Self-assembled structures, such as capillary blood vessels with vascular endothelial cells, can be formed.

Example of co-cultured liver tissue with sinusoidal network
*green: anti-albumin antibody (Hepatocyte)
*red: anti-CD31 antibody (Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells)
Diverse Cell Sources
- Patient-derived cells
- Cell lines
- iPSC / ESC-derived cells
- etc.
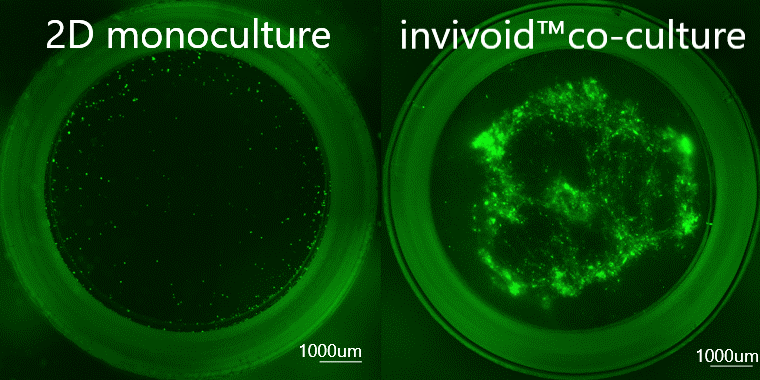
Example of culturing patient-derived primary cancer cells. Cancer cells grew only in invivoid® co-culture model using inexpensive growth factor free medium (DMEM).
Methodology 2 :
CMF(Collagen Microfiber) Method
How it works

Homogenization and lyophilization of collagen sponge creates highly dispersible fragmented collagen fibers.
Unlike the CVA method, this method produces thick, high collagen density tissue.
Tissues up to 5 mm thick can be created in a single step, without the need to layer cells one by one.
Key Advantages
High cell support/water dispersibility
Unlike gelatin or collagen peptides that have been chemically degraded, CMF consists of fine fibers that maintain the inherent water-insolubility of collagen while significantly improving dispersibility.

Comparison with chemically degraded gelatin and collagen peptides
Fine fiber formation through the defibration of collagen
Easily dispersible in culture medium, ideal as a scaffold for cells

Observed images and calculated fiber thickness in optical microscope and scanning electron microscope
Enables the production of collagen-dense tissues with high thickness
Cells are dispersed to the interior and survive even in tissues thicker than 1 mm

3D cellular tissue section using cancer cells and fibroblasts
Thickness and stiffness are controllable
Thickness and stiffness can be controlled by changing the amount of CMF in the tissue

Elastic modulus when CMF amount is controlled and thickness/strength is changed. Cell position control and analysis such as migration progress measurement is also possible.
