© TOPPAN INC.
Tokyo – October 24, 2022 –Toppan (TYO: 7911), a global leader in communication, security, packaging, décor materials, and electronics solutions, and the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) have developed PQC CARD®, the world’s first smart card equipped with post-quantum cryptography,1 which is difficult for even a quantum computer to crack. The organizations have also successfully confirmed effectiveness by applying PQC CARD® to control access to H-LINCOS,2 a system for the secure long-term storage and exchange of healthcare data.
PQC CARD® uses CRYSTALS-Dilithium,3 a next-generation digital signature algorithm selected as a potential standard technology by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)4 in July this year. PQC CARD® was developed in collaboration with ISARA Corporation, a company with cutting-edge post-quantum cryptography technologies.
Toppan and the NICT will take advantage of this technology to advance development of quantum secure cloud technology5 that enables the secure communication, storage, and use of highly sensitive information. Going beyond smart card security, the two organizations will also target the establishment of safe and secure social infrastructure based on the creation of fundamental technologies that ensure security for day-to-day internet-based activities, including email, online shopping, cashless transactions, and online banking.
Part of the research was supported by two Japanese government programs: the Cabinet Office’s Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP) “Photonics and Quantum Technology for Society 5.0” and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications’ Research and Development for Construction of a Global Quantum Cryptography Network (JPMI00316).
Background
In today’s information-driven society, internet-based services such as email, online shopping, cashless transactions, and digital application forms are securely protected by digital signatures, authentication, and key exchange based on public-key cryptography6 as well as by data encryption based on symmetric-key cryptography.7
There is a risk, however, that cryptosystems widely used today will be vulnerable to attacks from quantum computers, a field in which R&D is moving at a rapid pace. Preparations are underway for migration to post-quantum cryptography that will be difficult to decipher even after quantum computers come into practical use. This migration is expected to progress on an unprecedented scale from 2025 onwards.
NIST is advancing the standardization of post-quantum cryptography technologies and in July this year announced the selection of the first group of quantum-resistant encryption tools. Migration to the selected public-key cryptographies is expected to be seen worldwide as they become de facto global standards. To address the cybersecurity risks posed by quantum computers, efforts to establish and advance the use of robust new cryptography technologies are already underway in the U.S., including a National Security Memorandum signed by President Biden in May this year.8
Complete migration to the new cryptographies is predicted to take about 10 years. This means prompt action is needed to keep pace with progress towards the practical use of quantum computers. To address these challenges, Toppan, the NICT, and ISARA have collaborated to pioneer the development of PQC CARD®, which is equipped with CRYSTALS-Dilithium, one of the post-quantum cryptographies selected by NIST. Effectiveness has been successfully confirmed by applying PQC CARD® for smart card authentication and digital medical record access control on H-LINCOS, which is operated by the NICT.
Based on the results, the organizations expect to be able to establish technology for equipping smart card systems with post-quantum cryptography and to advance the adoption of the cryptography to facilitate a smooth transition to encryption infrastructure for the quantum computing age. Toppan will continue to collaborate with the NICT on driving early adoption of post-quantum cryptography to create and maintain infrastructure for safe and secure information communication.
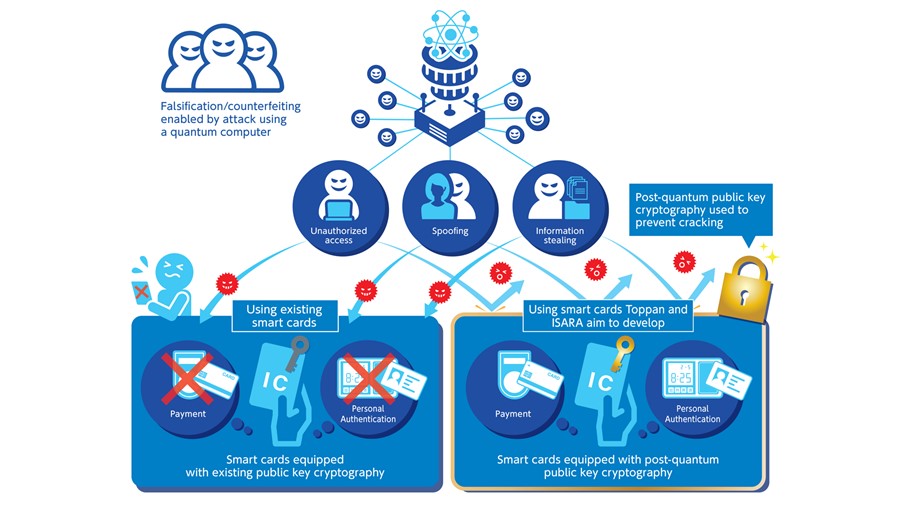
Features of PQC CARD®
・World’s first smart card equipped with CRYSTALS-Dilithium post-quantum cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography is encryption technology that is difficult for even a quantum computer to decipher. NIST has been screening potential candidates for standardization since 2017 and in July this year selected multiple methods, including CRYSTALS-Dilithium. The methods selected are expected to become de facto global standards.
・Ease of use maintained with no changes on the user side
Users do not need to replace hardware. Reader/writers, communication protocols, and the like for existing smart cards using current cryptography methods can continue to be used in the same way with PQC CARD®, delivering excellent authentication speed and performance.
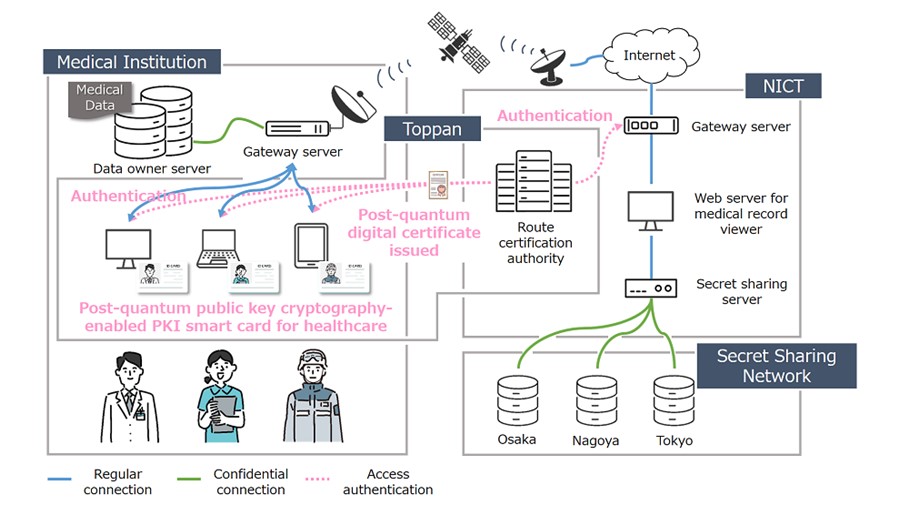
Overview of pilot test
Test period: August to October 2022
Objective: To confirm fundamental operation of healthcare professional authentication and access control in H-LINCOS using PQC CARD® and to identify technical challenges to address.
Details: PQC CARDs were used as HPKI (Healthcare Public Key Infrastructure) cards, the accreditation carried by healthcare professionals. Two-factor authentication for browsing electronic medical records was performed by combining smart card authentication with biometric authentication in the form of facial recognition. The encryption used for communication between the browser and the server was updated to CRYSTALS-Dilithium and its functioning was assessed. The pilot test evaluated improvement in the quantum resistance of the H-LINCOS system overall and its effectiveness.
Results: It was confirmed that only people with the proper authorization were able to access electronic medical records in accordance with their access rights. The test also confirmed improvement of quantum resistance and the effectiveness of H-LINCOS overall and identified the challenges to address for practical implementation.
Future activities
Toppan aims to launch full-scale provision of PQC CARD® and related systems in 2030, with limited practical use in sectors such as healthcare and finance in 2025. In collaboration with the NICT, Toppan will leverage the technology developed to drive the practical use of quantum secure cloud technology that enables the secure communication, storage, and use of highly sensitive information. The two organizations also intend to apply and expand the adoption of post-quantum cryptography beyond smart cards, as a fundamental technology for security on the internet, including email, online shopping, cashless transactions, and online banking as well as IoT systems and connected cars, for which technology is being established using existing cryptography methods.
The post-quantum cryptography tools selected by NIST include multiple encryption methods for public-key cryptography and digital signatures. Toppan and the NICT previously referred to these methods as “public-key cryptography,” but have revised this to “post-quantum cryptography,” in line with the terminology used by NIST.
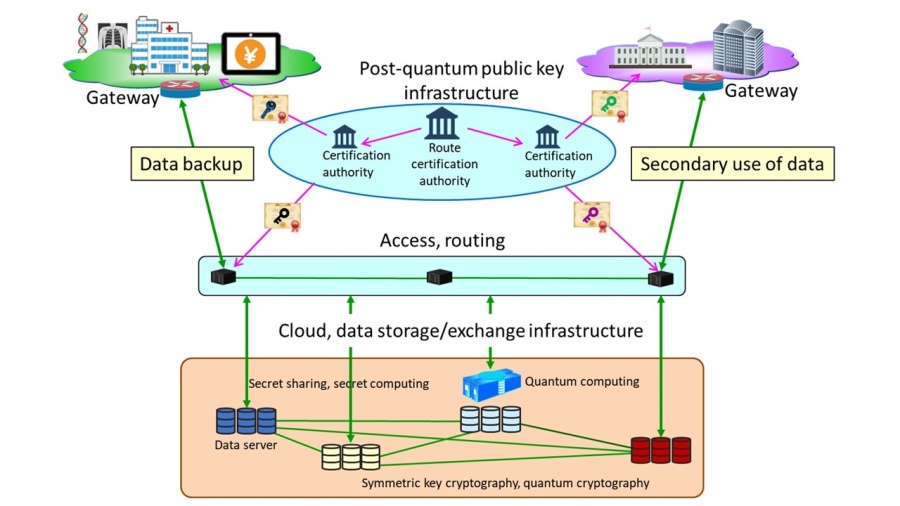
2. Healthcare Long-term INtegrity and Confidentiality protection System (H-LINCOS)
A long-term secure data storage and exchange system for healthcare that uses secret sharing and secure communication technologies to enable backup and mutual use by medical institutions of digital medical record data with high levels of security and availability. A related press release from the NICT can be viewed at https://www.nict.go.jp/en/press/2019/12/12-1.html.
3. CRYSTALS-Dilithium
A lattice-based public-key encryption method that is one of the digital signatures using post-quantum cryptographies selected by NIST.
4. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
A federal agency that promotes the establishment of standards for technology and industry in the United States.
5. Quantum secure cloud technology
A cloud technology that fuses quantum cryptography and secret sharing technologies to facilitate secure data communication, storage, and use. A related press release from Toppan can be viewed at https://www.toppan.com/en/news/2020/10/newsrelease201019e.html.
6. Public-key cryptography
A cryptography method that uses a pair of different keys for the encryption and decryption of information.
7. Symmetric-key cryptography
A cryptography method that uses the same keys for the encryption and decryption of information.
8. National Security Memorandum on Promoting United States Leadership in Quantum Computing While Mitigating Risks to Vulnerable Cryptographic Systems
https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2022/05/04/national-security-memorandum-on-promoting-united-states-leadership-in-quantum-computing-while-mitigating-risks-to-vulnerable-cryptographic-systems/
About Toppan
Established in Tokyo in 1900, Toppan is a leading and diversified global provider committed to delivering sustainable, integrated solutions in fields including printing, communications, security, packaging, décor materials, electronics, and digital transformation. Toppan’s global team of more than 50,000 employees offers optimal solutions enabled by industry-leading expertise and technologies to address the diverse challenges of every business sector and society and contribute to the achievement of shared sustainability goals.
For more information, visit https://www.toppan.com/en/ or follow Toppan on LinkedIn https://www.linkedin.com/company/toppan/.
About NICT
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) is Japan’s sole National Research and Development Agency specializing in the field of information and communications technology and is charged with promoting the ICT sector as well as research and development in ICT, which drives economic growth and creates an affluent, safe and secure society.
For more information, visit https://www.nict.go.jp/en/