Printing Technologies
TOPPAN’s
Five Core Technologies
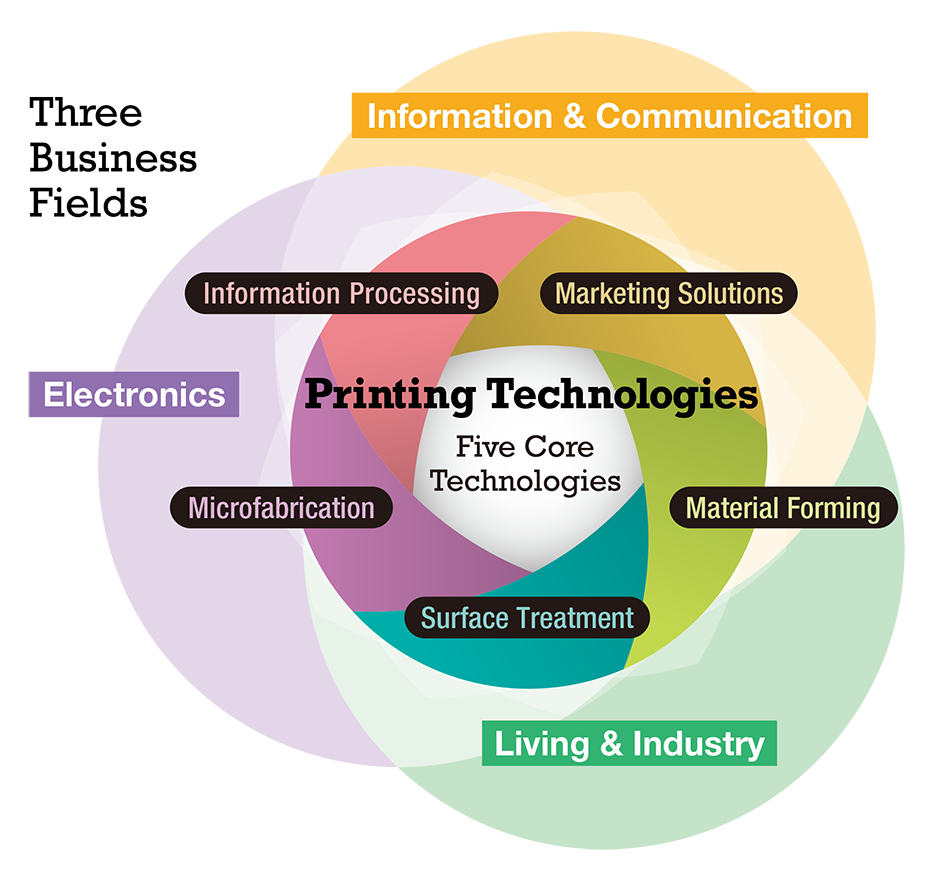
Over its long history, TOPPAN has evolved the printing skills that marked its origins into printing techniques, integrating and evolving them with a variety of knowledge, know-how, and processing technologies. This evolution has allowed TOPPAN to systematize its “printing technologies” as a unique resource. These printing technologies—information processing, microfabrication, surface treatment, material forming, and marketing solutions—represent five core technologies. Each possesses unique technical strengths and, when combined, can create new solutions. TOPPAN, using these printing technologies as a foundation, combines customer perspectives (market needs) and societal viewpoints (social issues) to provide total solutions that address various challenges. Furthermore, in the context of technological innovation and business expansion, TOPPAN is committed to enhancing and expanding its core technologies. We actively pursue new solution offerings through co-creation with universities, partners, startups, and other entities both domestically and internationally, with the aim of being a corporation that continuously generates social value.
Marketing Solutions
In 1904, the fifth year after our founding, we offered proposals for cigarette packaging designs by our in-house designers. Since then, we have strengthened our total solution capabilities in marketing and creativity areas, including establishing a Marketing Research Laboratory to conduct consumer awareness surveys. Recently, we have expanded our scope to include scientific approaches to psychology and cognition. To this end, we have been exploring universal design and established the Institute of the Formative Art and Shop Science Lab as part of our efforts.
Research and Analysis
We conduct analyses using various data resources such as social and lifestyle trends, household finances and consumption, and contact with media. We support the creation of various mechanisms and accompanying stories that drive customers to make purchases. We accomplish this by identifying the actions and processes leading to purchase decisions and the underlying mindsets, as well as measuring the effectiveness of communication with buyers at points of sale. Recently, we have also offered neurological research that measures and analyzes biological responses, such as brain waves and line of sight, to understand the needs of targets at a deeper, unconscious level.
Branding
Targeting the future vision for a brand, we analyze the current situation, identify challenges to address, and design value as part of brand strategy consulting that creates universal and perpetual value for the brands of regions and businesses. Our branding support service EHONDEAR™ fuses the real and virtual worlds to maximize new customer experiences and help brands establish their presence.
Back Office Coordination
We offer a system for managing promotional campaign office operations, handling everything from receipt of applications to inquiry responses, prize draws, and prize distribution, all centrally managed in a database. In addition to standard reports, we also provide prompt notifications according to escalation rules when taking non-standard actions.
Information Processing
We cultivated our security technologies through the printing of stock certificates and banknotes. We have also focused on digitizing text and image information and establishing color management technology in image processing. These technologies are utilized in the smart card business and content creation and distribution for electronic publishing, and are leading to new business models like digital archiving of cultural assets and promotional uses of augmented reality.
Security Technologies
We possess world-class security printing technology that has been developed since our founding and is used in the banknotes and passports of a number of countries. We use this technology to ensure continuous, safe, and secure management of increasingly diversified personal information and sensitive information in terms of both systems and processes. We also have sophisticated security technologies that encompass everything from analog to digital. These include advanced ID systems for issuance and authentication management of IDs for people and things, covering personal identification, verification of product authenticity, and traceability, as well as the establishment of robust cybersecurity systems.
Color Management
Color management is a technology for adjusting colors to take into account the difference in appearance between monitor screens and printed materials, and for conveying the correct colors of real objects on the monitors of devices of different types. Use of this technology can support digital transformation of business operations, such as by enabling online negotiations and color proofing. It is also expected to have applications in new fields such as emergency medicine and online medical consultations.
VR/AR
Augmented reality (AR) technology augments the real world by superimposing computer graphics onto it, while virtual reality (VR) employs not only video, but also sound and touch to immerse users in a virtual world. With advances in information and communications technology and the proliferation of communication networks, these technologies, which project spaces as if they were real, are expanding their applications to include games and other entertainment, as well as training and simulations through virtual experiences. Cross reality (XR) refers to technologies that fuse the real and virtual worlds, allowing for the perception of non-existent entities. Besides AR and VR, this also includes mixed reality (MR), and substitutional reality (SR).
High-Definition Image Digitization Technology
We photograph tangible and intangible cultural and industrial resources at high resolution and digitize them. For example, historical buildings, sculptures, statues, and other three-dimensional objects are photographed in segments from different angles and combined. The collected digital data can be archived, preserving culture, art, historical sites, traditions, skills, and more in a multi-faceted manner as information in various media, such as high-definition images, videos, and sounds, for extended periods. Additionally, applications in historical document compilation, VR, replicas, and other high-value-added content are possible.
Microfabrication
We have developed our expertise in metal processing techniques essential for plate-making, such as etching (corrosion) and plating, and achieved the first domestic production of masks for mesa transistor manufacturing. In recent years, our microfabrication technology has been applied in the manufacturing of semiconductor photomasks, FC-BGA substrates, color filters for liquid crystal displays, and holograms.
Etching Technology
The wet process, conducted in a liquid phase, is a technique for dissolving and removing materials chemically or electrochemically. Due to its advantages, such as no alteration in processing, it is applied in the fabrication of electronic components where precise and fine detailing is required. This process is used in the manufacturing of metal masks, metal filters, and similar products.
Photolithography Technology
This technology involves exposing the surface of a material coated with a photosensitive substance (photoresist) to ultraviolet light or similar sources to create a patterned exposure. This process generates a pattern comprising exposed and unexposed areas. It is used in the manufacturing of liquid crystal display panels, semiconductor integrated circuits, semiconductor package substrates, and more.
Plating Technology
This surface processing technology forms a metal film on the surface of a base material, utilizing electrolytic plating (electroplating), which involves electricity, and electroless plating (chemical plating), which involves chemical reactions. It is used in the manufacturing of lead frames and semiconductor package substrates.
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment technology, born from the manufacturing process of packaging that wraps and protects products, is now widely applied to packaging for foods, pharmaceuticals, electronic products, and more. Beyond packaging materials, this technology is also applied in products such as our anti-reflective films and “ECO SHEET” décor materials.
Lamination Technology
This technology, which bonds thin films together, includes dry lamination using heat/pressure adhesion, non-solvent lamination using adhesives without organic solvents, and extrusion lamination, where resin is melted and extruded onto the film for bonding. It is widely used in food packaging materials, toiletries, and more.
Coating Technology
This involves forming a thin layer on a substrate to impart functionality to films. There are two main types: wet coating, where the material is applied and dried in the air, and dry coating, conducted in a vacuum where the material is vaporized. It is used for various products, such as barrier films, anti-reflective films, and a range of electronic products.
Material Forming
TOPPAN, over the course of its involvement in the planning, development, and manufacturing of packaging materials, has not only handled printing on flat surfaces, but also evolved a variety of processing technologies, such as molding from resins in sheet form (vacuum molding and pressure molding) and printing on molded products. The numerous technologies cultivated here are applied to a wide range of products, including décor materials such as wallpaper and decorative laminates, mock-ups of product samples, and even components for plastic electronic devices.
Resin Molding Technology
Resin molding encompasses a variety of technologies, including injection molding, as well as hollow (blow) molding, and sheet (vacuum, pressure) molding. In addition to cost and design considerations, the method used is selected based on the specific application, such as use for various parts, containers, trays, and more.
Surface Decoration Technology
This technology involves applying surface treatment or special processing to packaging, which enables three-dimensional effects, a variety of embossed patterns, and glossiness. It is utilized across a wide range of fields, including food, confections, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, during plastic molding, decorative labels can be inserted into the mold and thermally bonded, enabling decoration not just on flat surfaces but also on three-dimensional structures. This is used for packaging and mock-ups.
